R & D platform
-
Industrial Production
-
Mechanism Study
-
Clinical Research
Neuric acid production by microorganisms such as microalgae
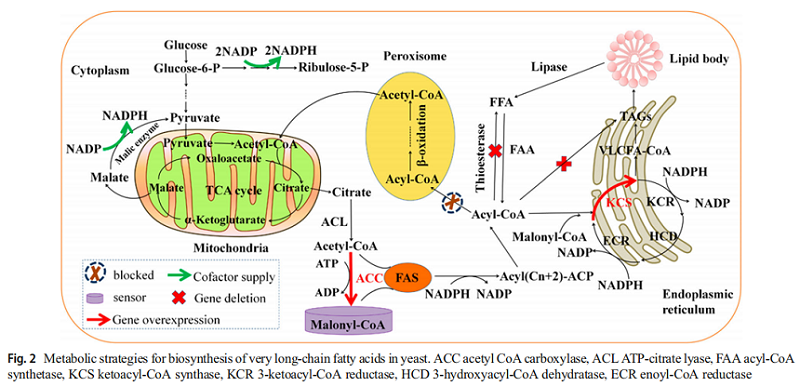
Neuric acid (NA) is a major component of myelin sheath. The decrease of NA level may reflect that the subideal state of myelin sheath in individuals has a high risk of developing into mental disorders. The use of neuroacid supplements has become an established method for the treatment of symptoms of several neurological diseases. In recent years, due to the rapid development of metabolic engineering and synthetic biology, heterogenous biosynthesis of VLCMFAS products in microorganisms has become a promising alternative. Several strategies to improve the production of neuroacids in microorganisms are introduced, including metabolic engineering, cell engineering and process engineering (Figure 2).
(1) Firstly, KCS has substrate specificity for VLCFA. In addition to studying the substrate specificity and expression activity of KCS, optimizing the utilization and accumulation of fatty acids in cells can help regulate the composition of fatty acids and increase the content of neuroacids. In rapeseed breeding, erucic acid can be accumulated by reducing the activity of desaturase, thus making more C18:1 enter the fatty acid extension pathway. This method can be used for the accumulation of neuroacids in microalgae and yeast metabolic engineering. Compact (customized optimization of metabolic pathways through combinatorial transcription engineering) is used to fine-tune gene expression in specific metabolic pathways. In addition, modular engineering can systematically eliminate the metabolic bottlenecks in the process of fatty acid synthesis, and can be used in the synthesis of neuroacids.
(2) Secondly, in yeast metabolic engineering, targeted or double-targeted NA biosynthesis pathways, such as mitochondria, peroxisomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and liposomes, may be an effective synthetic biological strategy. VLCFA was synthesized using acetyl coenzyme A and fatty acid activation form, lipid acyl coenzyme A and lipid acyl coenzyme A as substrates. In the production of neuroacids, it is very advisable to regulate glycolysis flux to fatty acid biosynthesis, especially to improve the level of precursors, delete competitive pathways and bypass the host to regulate metabolism. In addition, the production of VLCFA requires reducibility (NADPH) and energy (ATP) molecules, which are mainly derived from central metabolism. These factors can be balanced by redox engineering and can be applied to the production of neuroacids.
(3) Thirdly, metabolic switch and malonyl CoA sensor can dynamically regulate the biosynthesis of fatty acids and increase the potency of fatty acids by 2.1 times. A negative feedback regulating circuit with malonyl CoA sensor-actuator was used to regulate the biosynthesis of fatty acids. The circuit increased the potency and productivity of fatty acids by 34% and 33%, respectively. New paradigms of metabolic engineering may be used to control and optimize metabolic pathways that promote NA production. C/N ratio is a convenient control condition, it can make the target product get the most effective accumulation. Different culture methods, such as batch fermentation, fed batch fermentation and continuous fermentation, can also effectively improve the production of fatty acids.
In conclusion, exploring or directly evolving key enzymes with special substrate specificity from regenerated plants is an important basis for the production of neuroacids. In addition, using metabolic engineering technology to regulate metabolic flux through the biosynthetic pathway of recombinant nerve acid and develop oil-producing yeast for industrial production of nerve acid are also the focus of future research.
[1] Fan Y , Meng H M , Hu G R , et al. Biosynthesis of nervonic acid and perspectives for its production by microalgae and other microorganisms[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(9):1-9.


