R & D platform
-
Industrial Production
-
Mechanism Study
-
Clinical Research
Age-dependent changes in nervonic acid-containing sphingolipids in mouse hippocampus
Sphingolipids are a class of bioactive signaling molecules that regulate key cellular processes including cell growth, senescence and apoptosis. Sphingolipids have been implicated in age-related neurodegeneration. Previous studies have reported elevated ceramide levels in the brain of old rodents, but a systematic investigation of the impact of age on brain sphingolipid metabolism is still lacking. Here we quantified 17 key sphingolipid species in the hippocampus of young (3 months), middle-aged (12 months) and old (21 months) male and female mice. Lipids were extracted and quantified by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry; transcription of enzymes involved in sphingolipid biosynthesis was evaluated by qPCR.
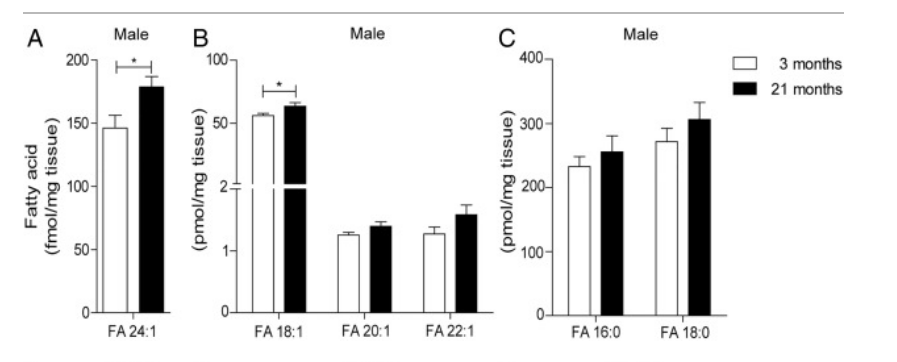
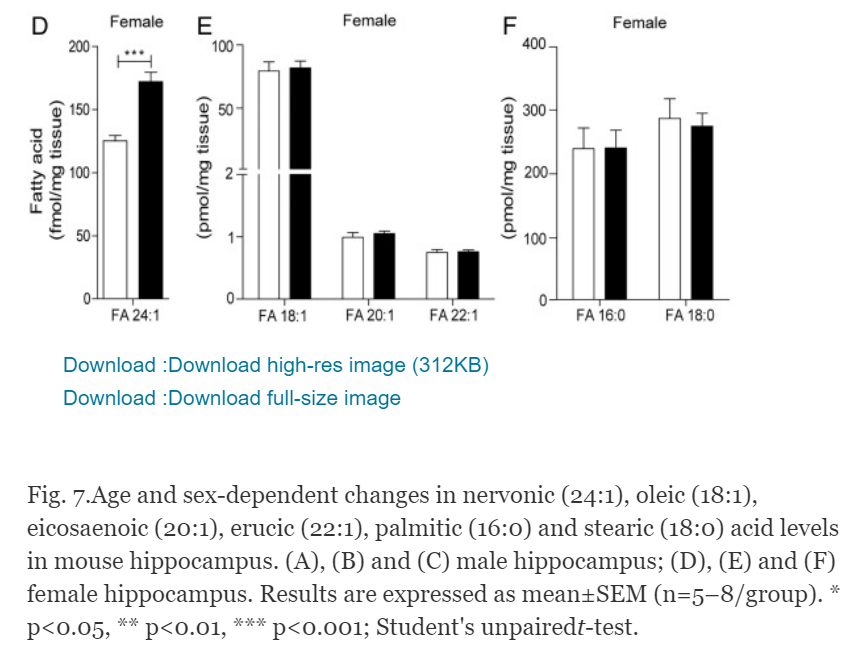
A common finding throughout our experiments was an elevation in sphingolipid species containing nervonic acid (24:1), which suggests that the production and the degradation of this long-chain monounsaturated fatty acid might be regulated by age. Consistent with this idea, we found that the content of non-esterified nervonic acid was higher in the hippocampus of 21 month-old male and female mice, compared to 3 month-old mice (Fig. 7A, D). A similar trend was seen with another monounsaturated fatty acid, oleic acid (18:1), in male but not female mice, whereas no change was observed in eicosaenoic acid (20:1) and erucic acid (22:1) (Fig. 7B, E), palmitic acid (16:0) and stearic acid (18:0) (Fig. 7C, F). The first committed step in the biosynthesis of nervonic acid is catalyzed by stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD), which converts stearic acid (18:0) into oleic acid (18:1). Elongase enzymes (ELOVL1 and ELOVL6 in brain) progressively insert two-carbon units to yield nervonic acid (24:1).
Age-dependent changes of multiple sphingolipid species - including ceramide (d18:1/18:0), sphingomyelin (d34:1), hexosylceramide (d18:1/16:0), ceramide (d18:1/24:0) - were found in mice of both sexes. Moreover, sex-dependent changes were seen with hexosylceramide (d18:1/18:0), ceramide (d18:1/22:0), sphingomyelin (d36:1) and sphingomyelin (d42:1). Importantly, an age-dependent accumulation of sphingolipids containing nervonic acid (24:1) was observed in 21 month-old male (p = 0.04) and female mice (p < 0.0001). In conclusion, the results suggest that aging is associated with profound sex-dependent and -independent changes in hippocampal sphingolipid profile. The results also highlight the need to examine the contribution of sphingolipids, and particularly of those containing nervonic acid, in normal and pathological brain aging.
A substantial body of prior work has documented a role for sphingolipids in aging and age-related disorders. A new and significant result of the present report is that nervonic acid-containing sphingolipids accumulate in the aging hippocampus of both male and female mice. Because of the previously described association between nervonic acid levels and cognitive impairment in AD, it will be important to examine the possible functional roles of nervonic acid-containing sphingolipids in the development of age-related neurodegeneration.
Reference
[1] Yuan H, Wang QH, Wang YY, Xie CM, Xie KQ, Zhao XL. [Effect of docosahexaenoic acid and nervonic acid on the damage of learning and memory abilities in rats induced by 1-bromopropane]. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2013. 31(11): 806-10.


